Corneal Evaluation
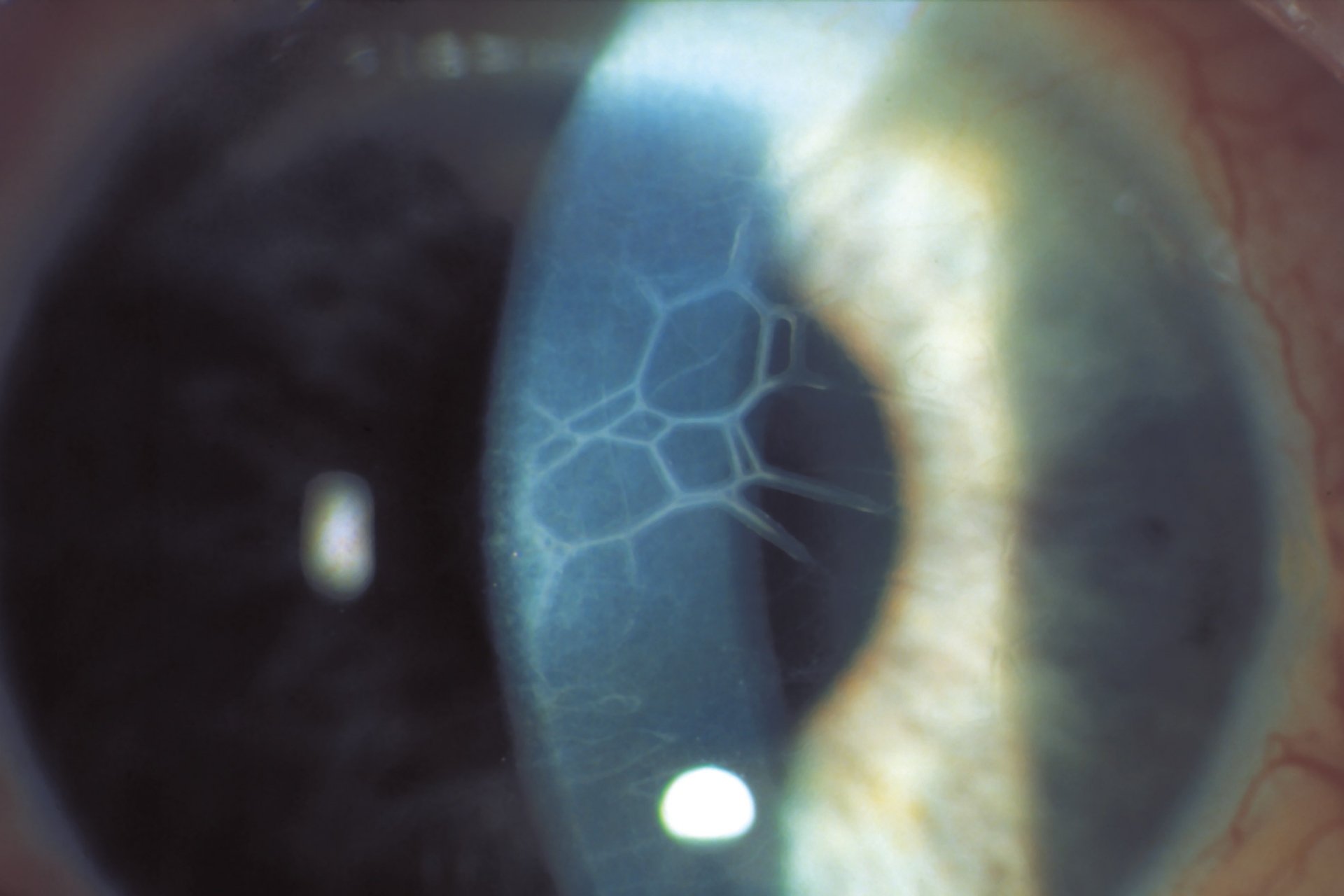
Slit lamps equipped with photography instrumentation are able to image the front of the eye, including the cornea. Dynamic viewing capabilities allow for multiple methods of analysis of corneal health.
Zeiss SL800
Slit Lamp Biomicroscopy
The health of the corneal epithelium can be examined more closely with vital dyes. Staining with sodium fluorescein and lissamine green are used for this assessment.
Much like the Zeiss slit lamp, the Takagi SM-70N is used to image the anterior eye including the cornea and is also equipped with a Wratten filter and cobalt blue lighting.
Takagi SM-70N
Slit Lamp Biomicroscopy
This instrument uses reflective rings to capture an infrared image of the anterior cornea, through which corneal diameter (HVID) can be measured. The scan captured provides quantitative data about the anterior cornea (Placido imaging) including:
Keratometry values
Corneal elevation
Refractive power
Tangential and axial maps
Shape descriptors such as e, p, Q and IS values
Two maps captured on the Medmont E300 can be compared using a difference map, which can be useful in showing change over time.
Medmont E300
Corneal Topography
Corneal tomography is captured using Schleimpflug imaging to provide data about the anterior and posterior cornea. This data includes:
Keratometry readings
Corneal thickness
Anterior and posterior corneal elevation
Corneoscleral height
Refractive power
Tangential and axial maps
Shape descriptors such as e, p, Q and IS values
Schleimpflug images (infrared photos and B-scans of the anterior eye)
Corneal diameter (HVID)
Corneal densitometry
Oculus Pentacam AXL Wave
Corneal Tomography, Ocular Biometry & Wavefront Aberrometry
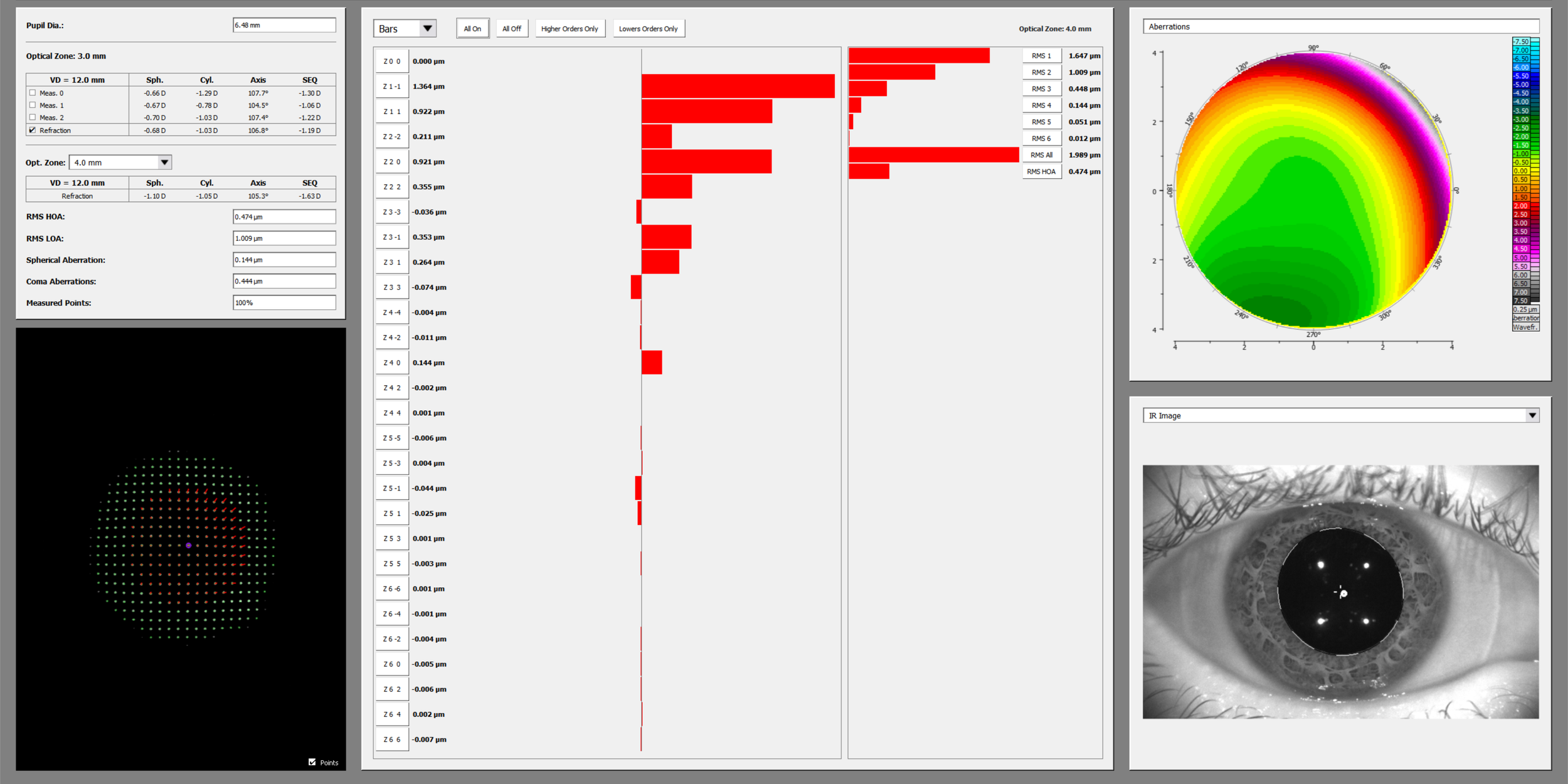
The Oculus Pentacam also measures wavefront aberrometry and can distinguish between corneal and total aberrations.
Much like the Oculus Pentacam, the Zeiss iProfiler Plus is used to measure the optical aberrations of the eye and can separate total aberrations from corneal.
Zeiss iProfiler Plus
Wavefront Aberrometry
Using sodium fluorescein reflection-based imaging, this instrument provides corneal and scleral readings including:
Keratometry values
Corneal elevation
Refractive power
Tangential and axial maps
Shape descriptors such as e, p, Q and IS values
Corneoscleral sagittal height
Eaglet Eye ESP
Corneoscleral Profilometry
Specular microscopy is a non-invasive means of collecting information on the cornea and specifically the corneal endothelium at the central, midperipheral and peripheral cornea. The Tomey EM-4000 analyses up to 300 cells of the corneal endothelium over a 0.25x0.54mm capture area, measuring:
Cell density (CD)
Average cell area (AVG)
Coefficient of variation of cell area (CV)
Percentage of hexagonal cells (6A)
Tomey EM-4000
Specular Microscopy
Anterior OCT captures information including corneal thickness (central and peripheral) and corneal transparency.
Heidelberg Spectralis
Anterior OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography)
Much like the Heidelberg Spectralis, this OCT captures corneal thickness and transparency data. It can also perform epithelial thickness mapping on the cornea.
Zeiss Cirrus 6000 Angioplex
Anterior OCT (Optical Coherence Tomography)
The Zeiss IOLMaster 500 provides keratometry readings based on an average of 6 separate readings.